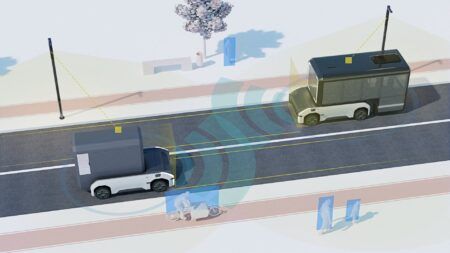
Baidu has launched its Apollo Go Robotaxi service in Cangzhou, Hebei province, extending robotaxi coverage to the downtown area of a city for the first time in China. The launch marks a significant milestone in Baidu’s development of autonomous driving technology and its aim to bring about the era of intelligent transportation.
With Apollo Go, people in Cangzhou can hail a robotaxi ride from train stations and other public spaces.
At first, the Apollo Go Robotaxi service in Cangzhou covers 55 pick-up and drop-off stations across the city, including train stations, schools, hotels, museums, business and industrial areas, and other public spaces.
The launch in Cangzhou comes after Baidu opened robotaxi services in a 130 square kilometre region of Changsha, Hunan province, in April this year. By servicing busy areas of Cangzhou, Apollo Go is making autonomous driving technology more accessible – and helpful – to users as they go about their daily lives.
People in Cangzhou can easily hail a free robotaxi ride through one click on Baidu Maps. For example, visitors to Cangzhou could hail a robotaxi after getting off the train to take them to their hotels. With safety a top priority, a human operator is assigned to each vehicle to take control of the autonomous system as a backup.
The launch of Apollo Go in Cangzhou follows years of extensive testing and trial operations across several cities. Technological progress now enables robotaxis to safely operate in busier areas that have more variables for the autonomous driving system to process. In addition to the operations in Changsha and Cangzhou, Apollo continues to conduct manned autonomous driving tests in Beijing, Chongqing, and other cities.
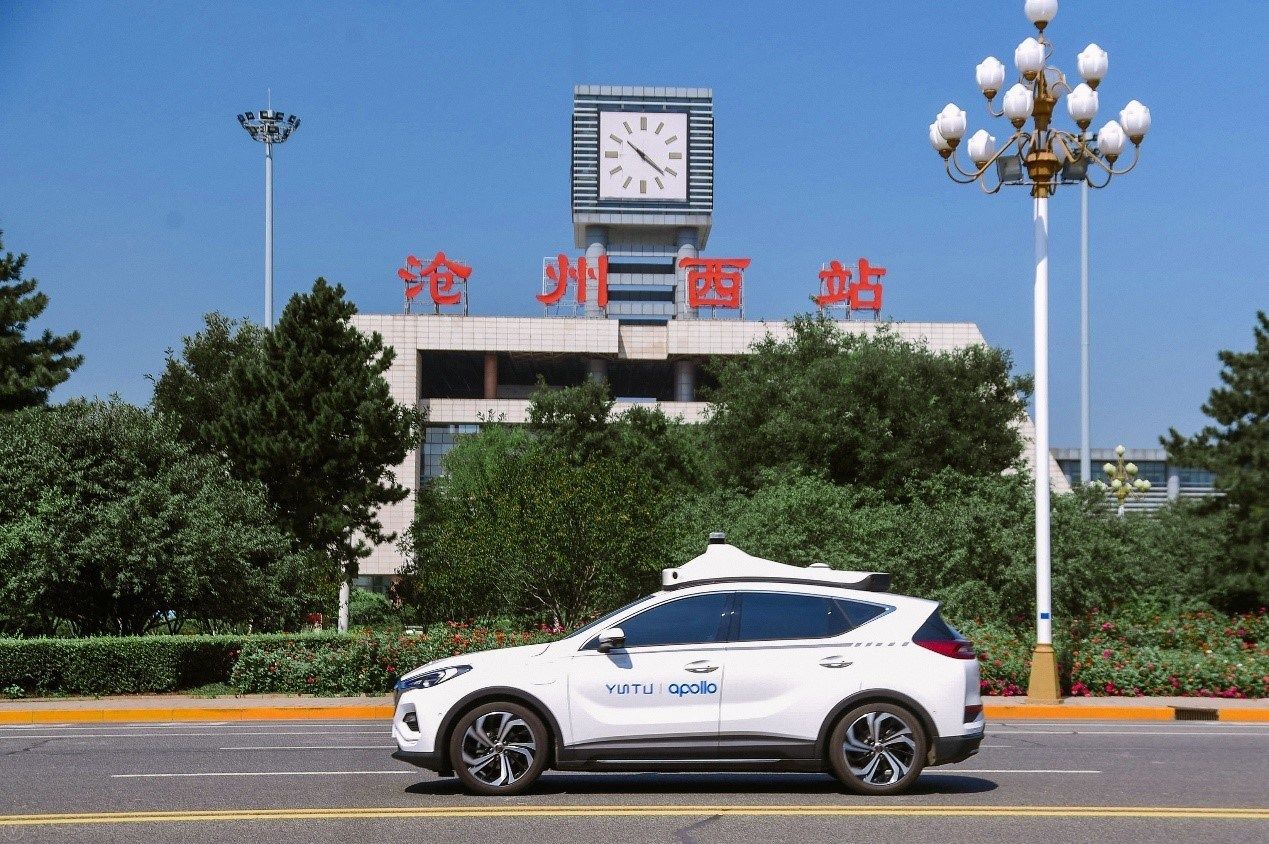

Cangzhou is a strategically important city, located within the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and on the Beijing-Shanghai corridor. In recent years, it has invested heavily in the development of intelligent network technology to facilitate the rollout of autonomous driving. Cangzhou was the first city in northern China to allow manned autonomous driving tests and has built one of the largest road networks for testing autonomous vehicles. Baidu reached a strategic cooperation agreement with Cangzhou to promote autonomous driving in September 2019. In November, the city opened certain road networks for manned autonomous driving testing, and Baidu Apollo’s fleet began testing with passengers shortly afterwards.
The ability of autonomous vehicles to operate in busier areas of a city is a result of Baidu’s continuous innovation. In 2019, Baidu Apollo and FAW Group jointly developed Hongqi EV, the first pre-installed and mass-produced L4 autonomous driving vehicle in China, and launched trial operations in Changsha in September.
Baidu Apollo is the world’s largest autonomous driving open platform. The Apollo fleet includes around 500 autonomous driving vehicles that have driven over 6 million kilometres and safely carried more than 100,000 passengers. Apollo now holds over 150 autonomous driving road test licenses and more than 1,800 intelligent driving patents globally.