Data-driven analysis of truck movement patterns from the fleet electrification study undertaken by the Ray and Geotab Inc can help guide state Departments of Transportation (DOTs) in the US to plan and fund electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure.
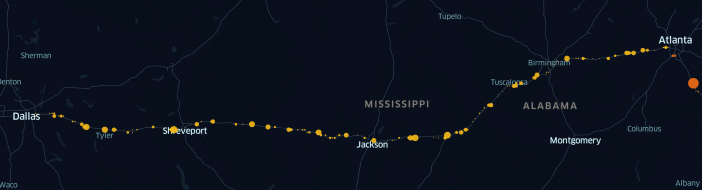
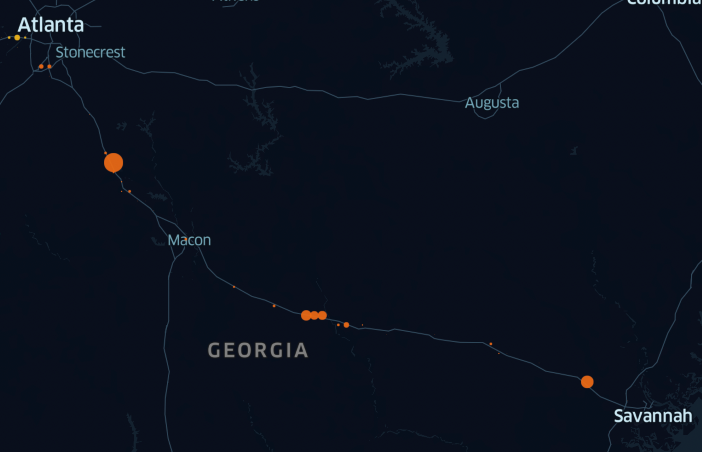
The Ray and Geotab performed the initial analysis on two pilot corridors: one regional route along the I-20 from Dallas, Texas to Atlanta, Georgia, and one local route, from the Port of Savannah, Georgia to the inland port in Atlanta, Georgia.
The analysis demonstrated different observed truck movement patterns for each of the two corridors. The regional route along the I-20 showed vehicles stopped at many, inconsistent locations along the entire route, while the local route revealed vehicles stopped at just a few distinct locations.
State DOTs are developing plans for EV charging infrastructure at 50-mile intervals along the US Interstate system. With 70% of all US freight being transported by medium- and heavy-duty vehicles, which contribute to nearly 24% of transportation greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs), fleet electrification will make a significant impact on total GHG emissions.
The Ray, utilizing Geotab telematics, can support states and local governments as they seek to determine the optimal locations and design for charging stations for both passenger and freight vehicles. Observing real truck movement data, The Ray says it can also help determine where and what type of additional truck parking is needed for electrification.
“Our cooperation and data analysis with The Ray will support the strategic positioning of charging infrastructure to help achieve the highest probability of success from the first day of deployment which will in turn help expedite freight EV adoption,” says Charlotte Argue, senior manager of fleet electrification at Geotab.
Geotab’s data analysis can be overlaid with The Ray’s GIS roadside solar tool to identify optimal locations for the development of roadside solar. Utilizing the tools together, State DOTs have the opportunity to connect the demand of high-powered EV charging stations with the potential production of right-of-way (ROW) solar.
“Findings from our pilot corridors underscore the need for data from additional corridors throughout the country to set states up for success,” says Allie Kelly, executive director of The Ray. “The telematics technology from Geotab, together as an overlay to The Ray’s solar mapping tool, will help transportation planners start one step ahead by developing infrastructure how and where it’s needed most, and determining which locations are optimal for co-locating EV charging and solar arrays on the roadsides.”
The recently passed federal Bipartisan Infrastructure Law will begin funding historic investments in infrastructure to support advanced transportation, including US$5 billion for electrification and UJS$2.5 billion for alternative, low or zero-carbon fueling.
The Ray is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit charity and net-zero highway testbed, located on 18 miles of Interstate 85 between LaGrange, Georgia and the Georgia-Alabama state line.
Images: The Ray, Geotab, AdobeStock