Toyota’s automated driving software development company, together with five industry partners has successfully completed proof of concepts (PoC) demonstrating high definition (HD) map building for surface roads with relative accuracy of less than 20 inches (50cm).
In the collaborative PoCs, the Toyota Research Institute-Advanced Development (TRI-AD) verified two methods that are effective for HD map building to a level that is required for automated driving:
- Building map information for self-driving via map data derived from the cameras of ordinary vehicles as well as satellite imagery, without the use of conventional means of collecting data such as survey vehicles;
- Applying vehicle data from TRI-AD’s Automated Mapping Platform (AMP) to other companies’ platforms by converting data formats and applying correcting algorithms.
 By using the results of these PoCs, it is expected that the delay in updating HD maps for automated driving can be shortened, areas of HD map coverage can be expanded quickly, and costs to build and maintain the HD maps can be substantially reduced.
By using the results of these PoCs, it is expected that the delay in updating HD maps for automated driving can be shortened, areas of HD map coverage can be expanded quickly, and costs to build and maintain the HD maps can be substantially reduced.
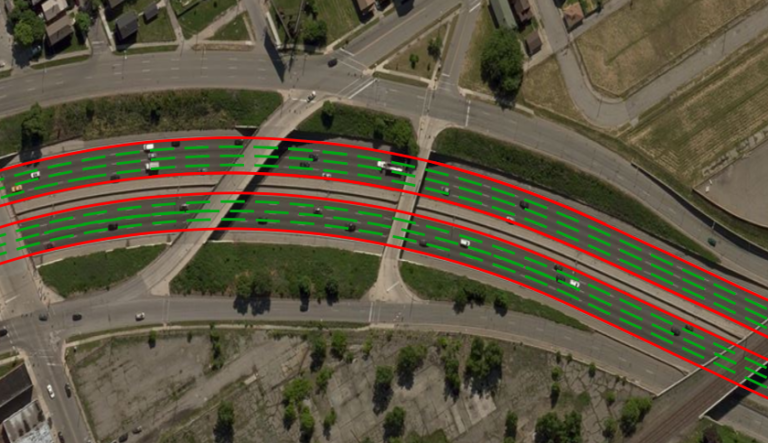
Maxar Technologies, a trusted partner and innovator in earth intelligence and space infrastructure, Japan’s leading IT services provider NTT DATA Corporation, and TRI-AD are collaborating on a PoC to build automated HD maps using the highest-resolution commercial satellite imagery. The PoC demonstrates it is now possible to automatically extract the required map information by analysing and removing and correcting non-map image pixels such as automobiles, shadows, and occlusions due to the inclination of buildings in satellite imagery. Maps with a relative accuracy of 10 inches (25cm) were created in Tokyo, as well as six cities globally, and were verified to be useful for self-driving purposes.
TRI-AD has successfully conducted a camera-based HD mapping initiative using Carmera’s road intelligence platform. The collaboration used consumer-grade ‘dashcam’ drive recorders to detect and place key road features such as lane markings, traffic signals and signs, in Tokyo and two cities in the USA. The project achieved a relative accuracy of 16 inches (40cm) for key navigation features; a major advance in camera-only detection. TRI-AD’s work with the company used the same hardware-agnostic computer vision and processing technology as Carmera’s Real-Time Events and Change Management engine, which detects, validates and delivers navigation-critical updates to its regenerative HD mapping system in minutes rather than months.
TRI-AD also collaborated with location technology specialist TomTom on a PoC that showed that lower-class roads (urban roads), including lane markings necessary for automated driving, could be successfully created or updated in near real-time on TomTom’s HD map. The solution was achieved by verifying the reliability of the vehicle data collected by TRI-AD’s AMP, and then converting it for input into TomTom’s cloud-based transactional mapmaking platform.
 TRI-AD has also collaborated with location data and technology developer Here Technologies’ on another PoC where, by correcting the positional errors in the vehicle data collected by TRI-AD, Here was able to automatically create surface road maps using its advanced ‘Self-Healing’ technology. By using only vehicle sensor data, Here ingested the data into its platform and automatically generated HD maps including lane level information required for automated driving.
TRI-AD has also collaborated with location data and technology developer Here Technologies’ on another PoC where, by correcting the positional errors in the vehicle data collected by TRI-AD, Here was able to automatically create surface road maps using its advanced ‘Self-Healing’ technology. By using only vehicle sensor data, Here ingested the data into its platform and automatically generated HD maps including lane level information required for automated driving.
“I’m very pleased to announce the results of the PoCs with our partners,” said Mandali Khalesi, VP of automated driving strategy and mapping at TRI-AD. “We got a step closer to a future where automated driving becomes a safer and more accessible technology for all.”