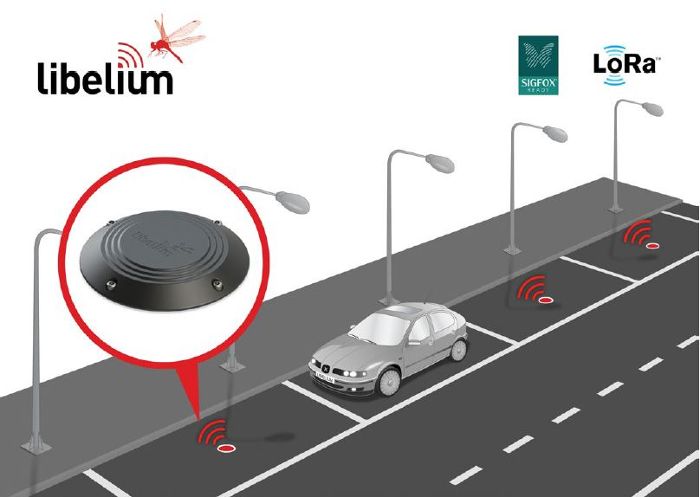
Aiming to meet the growing demand for greater precision in smart parking devices, the Spanish manufacturer of Internet of Things (IoT) hardware, systems and services, Libelium, has integrated radar detection technology into its parking space availability sensors.
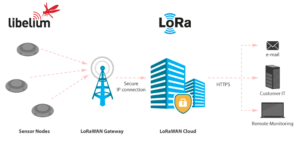
Libelium is already well known for its use of dual detection systems in its Smart Parking Sensor Node device. The main method uses a 3-axis magnetic sensor to detect vehicles, with a support system that uses the company’s cloud-based software to evaluate the wireless node’s received signal strength indication (RSSI) for Long-Range Wide-area Network (LoRaWAN) communications. If a car is parked over the sensor, the system detects the weaker power of the received wireless signal. Libelium’s new Smart Parking Node improves detection and stability performance due to an integrated radar sensor that allows precise detection (99%) of vehicles parked over the device, which then sends that data to the cloud through the LoRaWAN network.
Radar technology offers improved performance compared to traditional magnetic or infrared detection, as radar-based parking devices are not vulnerable to electromagnetic interference nor do they give false positives for vehicles parked near or in double rows. Their performance is more consistent in any weather or luminosity condition, more stable in long–stay parking cases, and they are not affected by the close proximity of traffic movements, such as passing buses or heavy trucks. The maintenance of radar parking sensors is also much easier as they are not affected by dirt, dust, rain, snow, ice or oil spills.
The use of the latest IoT technologies when applied to the detection of parking spaces can reduce the number of vehicles looking for an available spot, increase traffic flow, save fuel, decrease CO2 emissions, and improve the general driving experience and habitability of cities. In addition, smart parking devices are in high demand by municipalities aiming to monitor violations and check rotation levels in restricted parking areas, such as taxi ranks, loading and unloading bays, electric vehicle (EV) recharging spaces, and disabled areas. The first ‘real-world’ deployment of Libelium’s new radar sensors is currently taking place across the city of Huesca in northern Spain, where 190 nodes are being installed to detect the occupation of parking spaces for disabled people.
The nodes provisioning has been enormously improved, now delivered with default time settings and also unique LoRaWAN identifiers and keys, allowing the registration in the LoRaWAN network server at any one time. The new smart parking platform also provides over-the-air setup to remotely configure parameters, reducing installation times. Smart parking devices are registered in the Libelium Services Cloud Manager before leaving the factory. They can also be used in combination with the company’s Cloud Bridge to send data directly to any of the compatible platforms, making it easier and faster to create any parking management application.
David Gascón, co-founder and CTO of Libelium, noted, “Radar technology avoids the miscalibration problems that can be experienced with other types of technology, as the system is able to ‘see’ objects on top, when lots are occupied.”
“Connected mobility standards are no longer a vision for the future,” said Maxime Flament, 5GAA’s chief technology officer. “The solutions on show are ready to be deployed today and have huge industry momentum based on the forthcoming 5G capabilities. C-V2X technology is a key foundation for a safe and sound driving environment for pedestrians, bicyclists, motorcyclists, cars and commercial heavy trucks. Global field testing is already in its very final stages and the first solutions are now commercially available from multiple suppliers.”